Home » What We Treat » Mental Health Disorders We Treat » Personality Disorders » Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
At South Coast Behavioral Health, we understand the impact borderline personality disorder (BPD) can have on someone’s life. Our anxiety treatment services focus on the individual, ensuring a unique path to recovery suited to the needs of each client.
We're here because we've been there
After filling out this form, our admissions team will contact you at the number provided.
"*" indicates required fields
South Coast Behavioral Health is a safe and reliable source of borderline personality disorder (BPD) treatment for all.
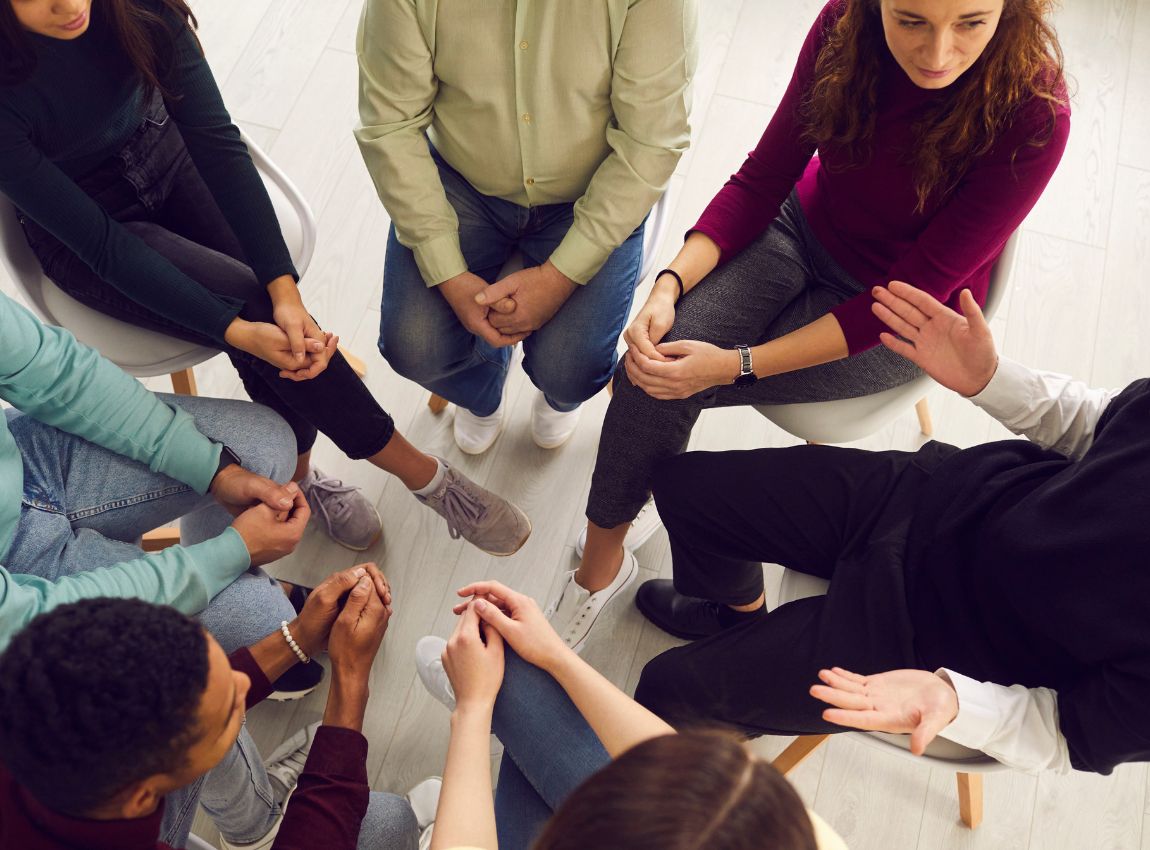
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a mental health disorder marked by strong emotions, unstable connections with others, and impulsive actions. It disrupts self-perception and social interactions, resulting in obstacles in daily routines. Borderline Personality Disorder is frequently misconstrued; it’s vital to identify its signs and appropriate therapies. Here, we will explore the significance of BPD symptoms, what leads to it, the accessible treatments, and different approaches that can aid individuals in handling their symptoms and enhancing their quality of life.

What Is Borderline Personality Disorder?
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a mental health condition that causes consistent fluctuations in emotions and behaviors as well as challenges in self-perception and relationship dynamics. Erratic emotions and impulsive choices commonly lead to tumultuous relationships and struggle with managing everyday tasks for those with BPD. The signs of the disorder often become apparent in early adulthood and may involve fears of being left alone or abandoned, emotional instability, and engaging in self-harm behaviors. Understanding Borderline Personality Disorder is essential for accessing effective treatment options, such as therapy and medication, which can help manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
How Does BPD Affect Daily Life?
Living with Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) can have an impact on everyday life. BPD can cause emotional ups and downs and challenges in relationships with others. People with BPD might struggle with managing their emotions and completing responsibilities due to sudden mood shifts. Impulsive actions, like substance misuse or self-injury, can add complexity to their daily routines. The emotional rollercoaster often leads to struggles at work or school, creating a cycle of stress and anxiety that affects overall well-being. Controlling triggers and actively pursuing therapy both play roles in enhancing daily performance and emotional health.
Diagnostic Criteria
The DSM-5 outlines specific criteria for diagnosing borderline personality disorder (BPD). To receive a diagnosis, an individual must exhibit at least five of the following symptoms, which must cause significant distress or impairment in functioning:
- Feeling anxious and making frantic attempts to prevent being alone, whether it's real or just in your mind.
- Experiencing a cycle of fluctuating and intense connections with others that switch between admiration and criticism.
- A low sense of self-perception that is notably shaky or inconsistent.
- Impulsive behaviors that could be harmful to oneself (i.e., spending and substance abuse).
- Repetitive acts of self-harm or life-threatening actions indicative of inner turmoil and distress.
- Emotional fluctuations caused by reactions to mood changes.
- Experiencing a void within oneself.
- Experiencing frustration or finding it hard to manage feelings of anger effectively.
- Feeling temporarily paranoid due to stress or experiencing detachment symptoms.
BPD vs. Other Personality Disorders
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) shares some similarities with other personality disorders, but it is distinct in its symptoms and impact on daily life. Unlike conditions such as narcissistic or antisocial personality disorders, which may involve a lack of empathy, BPD is characterized by intense emotional instability and unstable relationships.
Key differences include:
Emotional Dysregulation: BPD involves changes in mood and strong emotional reactions compared to other personality disorders that may show more consistent emotional behaviors.
Relationship Patterns: Individuals suffering from BPD often experience unstable relationships and how they view others, which can create shaky interpersonal interactions.
Impulsivity: Impulsivity is often observed in people with personality disorders. However, it appears more pronounced and is associated with emotional upheavals in individuals with BPD.
We are open 24 hours per day, 7 days per week, 365 days per year.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder?
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) presents a range of signs and symptoms that significantly impact an individual’s emotional and relational stability. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and effective treatment. Common signs of BPD include:
- Intense emotional instability: Rapid mood swings lasting from a few hours to days.
- Fear of abandonment: Extreme reactions to perceived or real separation.
- Unstable relationships: Intense relationships that fluctuate between idealization and devaluation.
- Impulsive behaviors: Reckless actions such as substance abuse, unsafe sex, or binge eating.
- Self-harm: Engaging in self-injurious behaviors or suicidal thoughts.
- Chronic feelings of emptiness: A pervasive sense of void or lack of purpose.
- Intense anger: Difficulty controlling anger, often followed by shame or guilt.
What Causes BPD?
Borderline Personality Disorder is thought to result from a mix of predispositions and influences from the environment and biology working together in tandem. Understanding these reasons can play a crucial role in creating successful treatment approaches and providing necessary assistance to individuals grappling with the condition.
Genetic Factors: Research has shown that genetics play a role in BPD, with estimates of heritability ranging from 40% to 60%. Studies involving families demonstrate that individuals with a background of BPD are more susceptible to developing the condition due to a genetic inclination.
Environmental Factors: Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs) like physical abuse and neglectful surroundings during formative years can play a crucial role in the onset of borderline personality disorder. Furthermore, being raised in an unsupportive environment can intensify emotional fragilities.
Biological Factors: Changes in the structure and function of the brain are noticeable in people with BPD. They are often linked to how emotions are managed and impulse control. Neurotransmitter imbalances, specifically concerning serotonin, can contribute to BPD symptoms and behaviors associated with the disorder.
Understanding these factors can play a crucial role in creating successful treatment approaches and providing necessary assistance to individuals grappling with the condition.
How Is Borderline Personality Disorder Treated?
Treatment for BPD is on a case-by-case basis. People often receive a blend of therapy sessions and prescribed medications to manage their symptoms effectively.
Psychotherapy
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), known for its emphasis on managing emotions and improving interactions, stands out as a top choice for BPD treatment. Other forms of therapy that may be considered include Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-focused therapy options.
Medication
Currently, there are no medications approved exclusively for BPD; however, doctors may recommend certain pharmacological treatments, such as antidepressants, mood stabilizers, and antipsychotics, to help alleviate anxiety, depression, and impulsivity. These medications can assist in controlling these symptoms.
Anti-Depressants
Antidepressants are drugs mainly prescribed for treating depression issues and anxiety disorders while also helping with personality disorders like BPD by regulating brain neurotransmitters. Antidepressants are categorized into several types, each with distinct mechanisms of action and applications. Here are the main types:
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs): These are the most commonly prescribed antidepressants known for their effectiveness and relatively mild side effects. Examples include fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and citalopram (Celexa).
Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs): Similar to SSRIs, SNRIs target both serotonin and norepinephrine. They may be more effective for certain individuals, with examples like venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta).
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): An older class of medications, TCAs are effective but often have more side effects. Common examples include amitriptyline and imipramine.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): These are rarely used due to potential serious side effects and dietary restrictions. Examples include phenelzine and tranylcypromine.
Atypical Antidepressants: This category includes newer medications that do not fit neatly into other classes, such as bupropion (Wellbutrin) and mirtazapine (Remeron).
Mood Stabilizers
Mood stabilizers are medications prescribed by psychiatrists to control emotional fluctuations linked to BPD and other mood disorders. They assist in balancing emotional peaks and valleys to establish a more consistent emotional foundation and are commonly combined with other therapies to lessen impulsiveness and emotional instability.
Common mood stabilizers include:
Lithium: Often the first-line treatment for bipolar disorder, lithium helps stabilize mood and prevent manic episodes. It is available in forms such as lithium carbonate and lithium citrate.
Valproate: Also known as divalproex or valproic acid (Depakote), this anticonvulsant is effective in managing mood swings and preventing manic episodes.
Carbamazepine: Marketed as Tegretol, this anticonvulsant is used to treat mania and mixed states, especially when lithium is ineffective.
Lamotrigine: Known as Lamictal, this medication is particularly effective for the depressive episodes of bipolar disorder.
Antipsychotics: Certain antipsychotic medications like olanzapine (Zyprexa) and quetiapine (Seroquel) can also function as mood stabilizers, helping to manage mood fluctuations.
Wondering if Your Insurance Covers Mental Health Treatment?
Strategies for Self-Help
Effective methods for dealing with borderline personality disorder can greatly improve health and well-being. Here are some helpful tips:
- Incorporating mindfulness into your routine can help you stay focused and calm.
- Regular exercise is also beneficial for reducing stress and maintaining a balanced lifestyle.
- Establishing a schedule and writing in a journal to work through your feelings are important practices for managing emotions.
- Fostering connections with others is essential for building emotional strength.
Professional Help for Borderline Personality Disorder
Getting assistance from experts for managing and recovering from borderline personality disorder is crucial for treatment. The usual approach includes a mix of talk therapy and prescribed medications personalized to suit the individual’s requirements.
Qualified mental health specialists like psychiatrists and psychologists offer support. Therapeutic methods such as Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are often employed to tackle fluctuations and relationship challenges, while medications can aid in handling particular symptoms such as anxiety or depression.
When Should You Get Help for BPD?
Recognizing when it’s time to seek support for borderline personality disorder (BPD) is key to managing it effectively. Counseling or therapy may be necessary if you’re going through emotional turmoil, self-destructive habits, and relationship challenges. If your symptoms start affecting your life or causing crises, it’s crucial to reach out to a mental health expert. Early intervention can greatly boost your well-being and quality of life; hence, prompt action is important when symptoms worsen.
If you or someone you know is struggling with mental health issues, South Coast Behavioral Health is here to help. We have a team of experts who can assist you in your recovery journey. Contact us today to learn more and begin your journey to healing from mental illness. You don’t have to live with BPD symptoms any longer. Mental health care can help. Call us today!
Frequently Asked Questions
About Mental Health Treatment
What is the most widely used treatment for mental disorders?
Psychotherapy paired with medication is the most effective way to promote recovery. Examples include: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy, Exposure Therapy, Dialectical Behavior Therapy, etc.
What is the most treatable mental illness?
anxiety disorders
What is the #1 most diagnosed mental disorder?
anxiety disorders
What is the hardest mental disorder to treat?
Borderline personality disorder historically has been viewed as challenging to treat.
What is the deadliest mental condition?
anorexia
eating disorder
What is the disorder for which people most often seek treatment?
Anxiety disorders. Depression, bipolar disorder and other mood disorders. Disruptive behavior disorders, such as oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder.
Get A Confidential Assessment From A Recovery Specialist
South Coast Behavioral Health offers outpatient and inpatient programs to address anxiety effectively by providing personalized treatment that incorporates evidence-based therapies and medication oversight along with individual or group therapy sessions. We provide support in a caring setting focused on improving mental health and facilitating healing.
Our addiction, mental health, dual diagnosis treatment centers in California:
Irvine, CA
We provide male-specific treatment for addiction and co-occurring mental health disorders within our medical detox and residential treatment centers in Irvine, CA.
Huntington Beach, CA
We provide female-specific treatment for addiction and co-occurring mental health disorders within our medical detox and residential treatment centers in Huntington Beach, CA.
Costa Mesa, CA
We provide male-specific treatment for addiction and co-occurring mental health disorders within our residential treatment center in Costa Mesa, CA.
Newport Beach, CA
We provide comprehensive care for those with primary addiction, primary mental health, and dual diagnoses within our PHP and IOP treatment facility in Newport Beach, CA.
Our dual diagnosis treatment center in Oklahoma:
Oklahoma City, OK
We provide comprehensive care for those with addiction and co-occurring mental health disorders within our inpatient and outpatient treatment center in Oklahoma City, OK.
Our treatment centers in California and Oklahoma offer a wide range of services and dedicated addiction specialists who will help you begin your journey. We believe in empowering real people to get real, lasting results in recovery. Contact us today to get started!
Let us help you take back your life.
You are the most important individual that we can help. You matter to us in ways that we cannot describe in words. Your life has value, and no matter how broken you think you are, we are here to help put the pieces back together.