With clinical anxiety rates in the United States at all-time highs, various drugs have naturally proliferated, each promising much-desired relief. When it comes to managing anxiety, the choice of medication can have profound implications on one’s quality of life. Xanax is the most popular pharmaceutical treatment for anxiety, but there are others as well. One of these is gabapentin. You may wonder what the differences between gabapentin and Xanax are; this article will seek to answer your questions.
What Is Gabapentin?
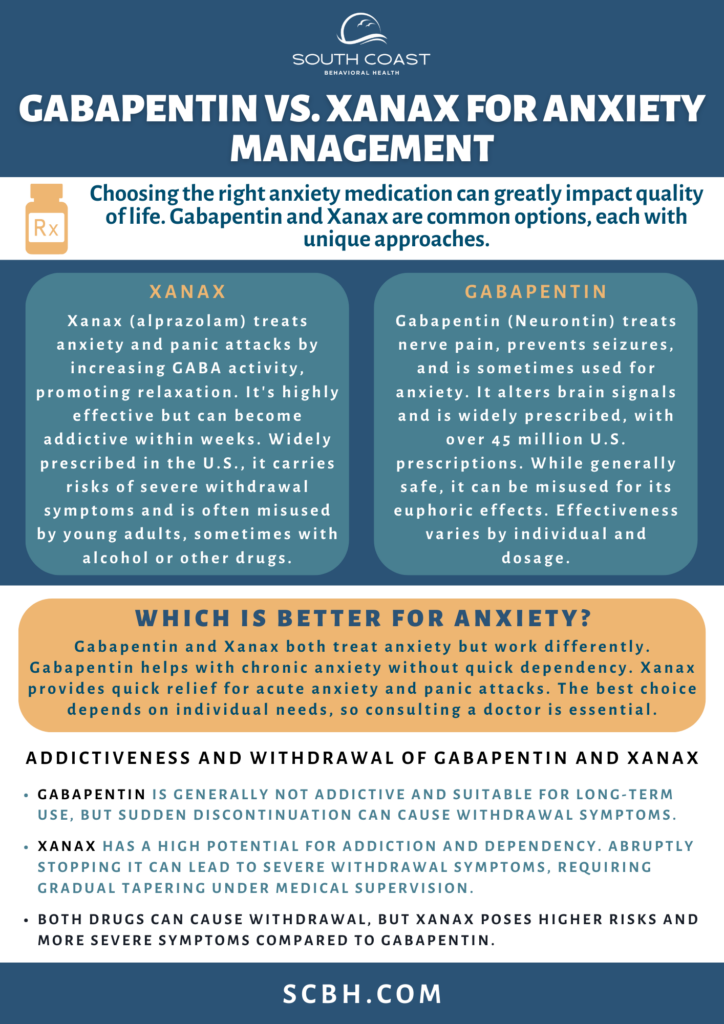
Gabapentin, also known by the brand name Neurontin, is a medicine often used to treat nerve pain and prevent seizures. It belongs to a group of drugs called anticonvulsants or antiepileptics. Gabapentin changes the way electrical signals move in the brain which affects how nerve cells communicate with each other.
Here are some important points about gabapentin:
- Approved Uses: It’s used not just for epilepsy but also for treating nerve pain from shingles and, unofficially, for anxiety.
- Prescription Rates: Gabapentin is the tenth-most prescribed drug in the United States, with over 45 million prescriptions.
- Potential for Misuse: Although it’s generally safe, there is a concern about gabapentin abuse, especially with opioids. This is because it increases feelings of euphoria.
- Effectiveness: Research shows that gabapentin helps reduce pain in various conditions like diabetic nerve pain and fibromyalgia. However, the effectiveness of the drug depends on the person and the dose they take.
What Is Xanax?
Xanax, also known as alprazolam, is a benzodiazepine medication mainly used to help people with anxiety and panic attacks. It helps calm the brain by affecting a brain chemical called GABA, which can make a person feel more relaxed, less anxious, and even sleepy. Xanax works quickly and is very effective, but if it’s taken for a long time, it can be addictive.
Here are some important points about Xanax:
- Addictive Potential: While Xanax is not an opioid, it rivals those drugs in terms of addiction. Xanax and other benzodiazepines can be very addictive. People might start relying on it in just a few weeks.
- Prescription Rates: It’s one of the medications doctors prescribe the most in the U.S., with millions of prescriptions given out every year.
- Withdrawal Concerns: If someone stops taking Xanax suddenly after using it a lot, they could have serious withdrawal symptoms, like seizures.
- Usage Demographics: Young adults sometimes misuse Xanax, often mixing it with alcohol or other drugs to increase its effects.
Gabapentin and Xanax: Which Is Better for Anxiety?
Gabapentin and Xanax are both medications used to treat anxiety, but they work in different ways and suit different types of anxiety. Originally designed to treat epilepsy, gabapentin helps stabilize electrical activity in the brain and reduce nerve pain. It’s increasingly used off-label for chronic anxiety because it doesn’t cause dependency as quickly as other drugs. On the other hand, Xanax, a fast-acting benzodiazepine, assists in relaxing the mind by boosting the effect of GABA, a natural calming agent in the brain. This makes it effective for acute anxiety and sudden panic attacks.
Each drug works differently, which is why the best choice depends on the specific needs and medical history of the individual. Consulting a doctor is crucial. Medical professionals can assess the nature of the anxiety, discuss potential side effects, and consider any personal health factors to determine the most appropriate medication.
Is Gabapentin Like Xanax?
Not really. While both drugs are prescribed to treat anxiety, they have totally different mechanisms and belong to different drug families. Gabapentin, an anticonvulsant, works by affecting certain calcium channels in the nervous system to calm nerve activity. This is different from benzodiazepines like Xanax (alprazolam), which work by enhancing the effect of the neurotransmitter GABA on GABA-A receptors, producing sedation, muscle relaxation, and anxiety relief.
Get confidential help from our addiction treatment specialists in Orange County. Call to join our rehab program today!
Call 866-881-1184Are Gabapentin and Xanax Addictive?
Gabapentin is generally not addictive. and it has a different side effect profile compared to benzodiazepines, making it a suitable option for long-term use under medical supervision.
However, if someone stops taking it suddenly, they might have withdrawal symptoms, which suggests it can be habit-forming, especially for those who have had issues with drug addiction before. It is also important to be aware of interactions, such as those involving gabapentin and alcohol, which can enhance sedative effects.
On the other hand, while Xanax is effective for short-term use, its potential for addiction and dependency is well-documented, posing significant risks for some patients. As research continues to evolve, patients and healthcare providers must stay informed about the best practices for treating anxiety, considering both the benefits and the risks associated with these medications.
Can I Take a Gabapentin with Xanax?
Taking Neurontin (gabapentin) and Xanax (alprazolam) together can be done, but it requires caution and should only be done under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
Both gabapentin and Xanax have sedative effects and can depress the central nervous system. When combined, these effects can be amplified, increasing risks such as:
Excessive drowsiness
Dizziness
Impaired coordination
Difficulty breathing
Increased risk of overdose
Because of these risks, doctors usually carefully monitor patients who take both, especially when starting or changing doses.
Bottom line: Don’t combine gabapentin and Xanax without medical advice. If you’re prescribed both, follow your doctor’s instructions closely and report any unusual side effects immediately. If you’re thinking about taking them together on your own, please talk to a healthcare professional first.
Do Xanax and Gabapentin Cause Withdrawal?
Both Xanax and Gabapentin can cause withdrawal symptoms, but their risks and the nature of their withdrawal processes are quite different. Xanax is known for its potential for addiction, even more so than other benzodiazepines. Users can develop a dependence on Xanax quite quickly, and stopping it abruptly after prolonged use can lead to severe withdrawal symptoms such as anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and even life-threatening conditions. This makes it crucial to taper off under medical supervision.
Gabapentin, though less addictive than Xanax, also carries a risk of withdrawal, particularly in those who have used it at high doses or for a long period. Gabapentin withdrawal symptoms can include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, pain, and sweating. While these symptoms are generally less severe than those from benzodiazepine withdrawal, they still require careful management and a gradual reduction in dosage to minimize discomfort and health risks.
Looking for quality substance abuse treatment that’s also affordable? South Coast accepts most major insurance providers. Get a free insurance benefits check now.
Check Your CoverageTreatment for Addiction and Co-Occurring Anxiety at South Coast Behavioral Health
At South Coast Behavioral Health, we provide a comprehensive approach to addiction and co-occurring anxiety treatment. Our dual diagnosis treatment covers everything from initial detox to extensive aftercare. We address the symptoms of gabapentin dependency or Xanax addiction as well as the underlying causes of anxiety. We tailor our treatment process to meet the needs of each client to ensure the most effective care. In doing so, we can help individuals achieve long-term sobriety and overall wellness.
Here are some of the therapies and treatments offered at SCBH:
- Detoxification: The first step is getting gabapentin and Xanax out of your system. Safe management and monitoring of withdrawal symptoms, particularly for those dependent on anxiety medications like Xanax.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): A form of psychotherapy that helps patients understand the thoughts and feelings that influence behaviors.
- Group Therapy: Facilitated sessions where patients can share experiences and learn from others facing similar challenges.
- Medication Management: Careful evaluation and administration of medications to balance effectiveness with minimal side effects.
- Holistic Therapies: Mindfulness-based practices like yoga, meditation, sound healing, and massage therapy.
- Aftercare Planning: Ongoing support after treatment to prevent relapse, including therapy sessions and community-based resources.
South Coast Behavioral Health’s integrative treatment model ensures that we address every aspect of an individual’s health. In doing so, we assist them in paving the way for a successful recovery. If you’re struggling with addiction and anxiety, our dedicated team is ready to provide personalized care tailored to your specific needs, from innovative therapies to ongoing support.
Take the first step towards a calmer, more fulfilling life. Contact SCBH today to learn more about our anxiety treatment options and start your journey to recovery.
- Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder with Gabapentin – PMC (nih.gov)
- Alprazolam – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)
- DailyMed – NEURONTIN- gabapentin capsule NEURONTIN- gabapentin tablet, film coated NEURONTIN- gabapentin solution (nih.gov)
- Benzodiazepines – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf (nih.gov)








